Why Blood Sugar Matters
Blood sugar levels play a crucial role in maintaining your overall health and energy levels. Whether you are living with diabetes, prediabetes, or simply want to take proactive measures for your health, understanding and managing your blood sugar is vital. When blood sugar levels are out of control, it can lead to both immediate discomfort and long-term complications, such as heart disease, nerve damage, or vision problems.
By learning to recognize the signs of high blood sugar (hyperglycemia) or low blood sugar (hypoglycemia), you can take timely action to prevent further health risks. This article explores the most common warning signs, their underlying causes, and practical tips to help you regain control over your blood sugar levels
Signs Your Blood Sugar May Be Out of Control
You’re Always Thirsty and Need Frequent Bathroom Breaks
Related : 9 Worst Foods for Your Eyes
Related : Top Foods for Healthy Hair
Excessive thirst, also known as polydipsia, and frequent urination, known as polyuria, are early indicators of high blood sugar. When glucose levels in your blood rise, your kidneys work overtime to eliminate the excess sugar. To do so, they pull water from your tissues, causing dehydration. This creates a vicious cycle where you feel compelled to drink more fluids and experience frequent bathroom visits.
- Tip: Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water, but focus on addressing the root cause of high blood sugar by consulting your doctor or a diabetes specialist. Proper blood sugar management can break this cycle.
Persistent Fatigue That Won’t Go Away
Feeling unusually tired, even after getting a full night’s sleep or taking a rest, may be a sign of blood sugar imbalance. High blood sugar levels can prevent your body from effectively converting glucose into energy. Conversely, low blood sugar can deprive your cells of the energy they need to function, leaving you feeling drained.
- Example: If you often feel fatigued after meals, it could be a sign of a spike or drop in your blood sugar levels. Pay attention to when fatigue occurs and share this information with your healthcare provider
Related : Exercise: 13 benefits of regular physical activity
Skin Changes You Shouldn’t Ignore
Your skin can provide early warnings of uncontrolled blood sugar. Common skin-related symptoms include

- Skin tags: Small, benign growths that tend to develop in areas of friction, such as the neck, underarms, or groin.
- Acanthosis nigricans: Dark, velvety patches that commonly appear on the neck, armpits, or other areas with skin folds.
- Dry or itchy skin: Caused by dehydration or poor circulation associated with high blood sugar.
- Blisters or slow-healing sores: A result of impaired skin repair processes.
Action Step: If you notice any persistent skin changes, schedule an appointment with your healthcare provider. Often, improved blood sugar control can resolve or significantly reduce these symptoms
Related : 12 Tips to Prevent Blood Sugar Spikes
Unexpected Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss, especially when you are not trying to lose weight, can be an alarming sign of uncontrolled blood sugar. When blood sugar levels are too high, your body excretes excess glucose through urine, leading to calorie loss. Over time, this can result in significant weight reduction.
- Tip: Incorporate a nutrient-dense diet and track changes in your weight regularly. Pair this with routine medical checkups to ensure that any weight fluctuations are properly addressed
Frequent Infections and Slow-Healing Wounds
High blood sugar levels can weaken your immune system, making it more difficult for your body to fight infections. Some of the most common infections include:
- Yeast infections: High sugar levels create an ideal environment for yeast to thrive.
- Urinary tract infections (UTIs): Often more common in individuals with elevated blood sugar.
- Gum infections: Leading to swollen or bleeding gums.
- Slow-healing wounds or sores: Impaired circulation and immune response delay the healing process.
- Practical Advice: Practice good hygiene, keep your blood sugar under control, and seek medical advice for recurring infections or wounds that take longer than usual to heal
Related : Health Benefits of Sweet Potatoes
Numbness and Tingling in Hands or Feet
High blood sugar can damage the nerves over time, a condition known as peripheral neuropathy. Symptoms include numbness, tingling, or a burning sensation in the extremities, such as the hands and feet.
- Preventive Measure: Regular foot and hand exams, coupled with diligent blood sugar monitoring, can help reduce the risk of severe nerve damage.
Vision Problems or Blurred Sight

Your eyes are particularly vulnerable to changes in blood sugar. Elevated levels can damage the tiny blood vessels in the eyes, a condition known as diabetic retinopathy. Early symptoms include:
- Blurred vision.
- Floaters or spots in your vision.
- Sudden vision changes, including partial or complete loss of sight
Take Action: Schedule annual eye exams to detect any damage early and prevent irreversible vision loss. Treating your blood sugar levels can also help slow the progression of eye-related issues.
Understanding Blood Sugar Levels
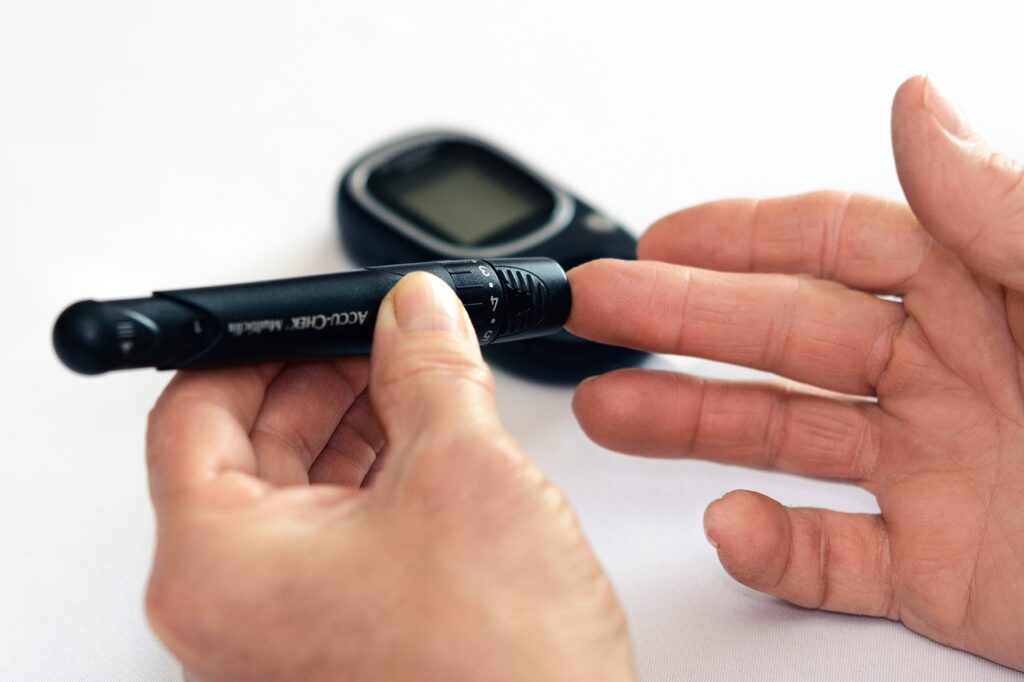
To manage your blood sugar effectively, it’s essential to know what normal levels look like:
- Normal fasting glucose: Below 100 mg/dL.
- Prediabetes range: 100–125 mg/dL.
- Diabetes diagnosis: 126 mg/dL or higher on multiple occasions.
Hyperglycemia (high blood sugar): Blood sugar levels exceeding 180 mg/dL after meals.
Hypoglycemia (low blood sugar): Blood sugar levels dropping below 70 mg/dL.
Monitoring these levels regularly can help you take prompt action when needed
Related : Ways to Find Relief From Eye Allergies
How to Take Control of Your Blood Sugar
- Adopt a Balanced Diet
Include low-glycemic foods, such as vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, in your meals.
Avoid processed carbohydrates and sugary snacks that cause rapid blood sugar spikes.
- Exercise Regularly
Physical activity helps improve insulin sensitivity and stabilizes glucose levels. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise, such as walking or cycling, on most days.
- Monitor Your Blood Sugar
Use a glucometer or continuous glucose monitor (CGM) to track your blood sugar levels. Regular testing helps you identify patterns and adjust your lifestyle or medication accordingly.
- Take Prescribed Medications
Follow your doctor’s recommendations for insulin or oral medications. Never skip doses or modify your medication without professional guidance.
- Stay Hydrated
Drinking water throughout the day supports kidney function and helps flush out excess glucose.
When to Seek Medical Help

Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe symptoms like confusion, dizziness, or fainting.
- Vision loss or sudden numbness in extremities.
- Persistent high blood sugar levels that do not respond to medications or lifestyle adjustments
Related : 14 Signs You’re Low on Vitamin B12
Practical Tips for Day-to-Day Management
- Plan Balanced Meals: Incorporate healthy fats, complex carbs, and lean proteins in your diet.
- Track Symptoms: Use a journal or app to log symptoms, meals, and blood sugar readings.
- Leverage Technology: Apps and CGMs can simplify blood sugar tracking and provide real-time insights.
- Stay Consistent: Small, consistent efforts lead to long-term health improvements
The Takeaway
Managing blood sugar levels is a journey that requires awareness, consistency, and proactive care. Recognizing the signs of uncontrolled blood sugar is the first step toward regaining control and preventing complications
Related : Proven Ways to Lose Weight Without Diet or Exercise
Actionable Advice: Begin with one small step today—whether it’s a healthier meal choice, a quick walk, or checking your blood sugar levels. These incremental changes can make a significant difference in your overall health and well-being
Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your health. With the right approach, you can effectively manage your blood sugar and lead a healthier, happier life
FAQs: Are Your Blood Sugars Out of Control? Signs to Look For
- What are the early signs of uncontrolled blood sugar?
Early signs include excessive thirst, frequent urination, persistent fatigue, unexplained weight loss, blurry vision, slow-healing wounds, and numbness or tingling in the hands and feet.
- How does uncontrolled blood sugar affect your skin?
High blood sugar can cause skin changes like dryness, itching, darkened patches (acanthosis nigricans), skin tags, and slow-healing sores or blisters due to impaired circulation and immune response.
- Can fatigue be related to blood sugar problems?
Yes, both high and low blood sugar can cause fatigue. High levels prevent glucose from being converted into energy, while low levels starve your cells of the fuel they need to function properly.
- What is the normal range for blood sugar levels?
- Fasting glucose: Below 100 mg/dL.
- Prediabetes range: 100–125 mg/dL.
- Diabetes diagnosis: 126 mg/dL or higher.
- How can I prevent uncontrolled blood sugar?
To prevent blood sugar spikes or dips:
- Eat a balanced diet with low-glycemic foods.
- Exercise regularly.
- Take prescribed medications as directed.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels.
- What should I do if my blood sugar levels remain high despite medications?
If medications are not effective, consult your doctor immediately. They may adjust your treatment plan, recommend dietary changes, or investigate other underlying conditions.
- When should I seek medical attention for blood sugar issues?
Seek medical help if you experience severe symptoms like confusion, fainting, vision loss, persistent high blood sugar despite treatment, or symptoms of diabetic ketoacidosis, such as nausea, vomiting, or abdominal pain