In this article
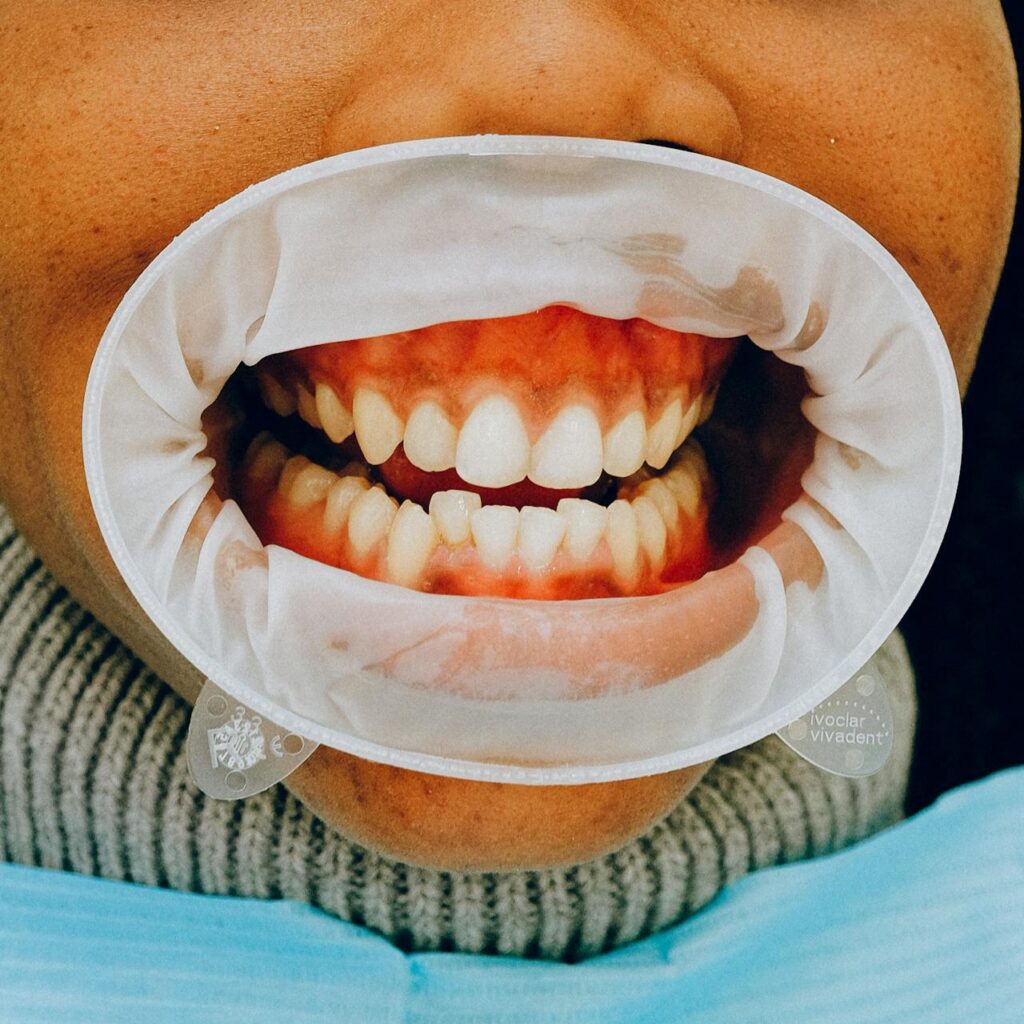
Bleeding gums, mouth, lips, or tooth sockets can result from various factors, including gum disease, mouth conditions, dental treatments, surgeries, or injuries.
Causes of Bleeding Gums
If your gums bleed after brushing your teeth, it might indicate gum disease due to plaque accumulation on your teeth and gums.
Gingivitis: This is the early stage of gum disease characterized by bleeding, redness, and swelling (inflammation) of the gums.
Periodontitis: This advanced stage occurs if gingivitis is left untreated, leading to:
- Loose teeth
- Bad breath
- Tenderness or discomfort when biting
- Receding gums (teeth appear longer)
If you suspect gum disease, seeing a dentist is crucial for early treatment to protect your teeth.
Preventing Bleeding Gums
To prevent gum disease and maintain healthy gums, consider the following tips:
- Brush your teeth after every meal for at least two minutes.
- Use dental floss daily; your dentist or pharmacist can guide you on this.
- If your gums are sore, opt for a soft toothbrush.
- Antibacterial mouthwashes might help, but consult your dentist or pharmacist first, as some medical mouthwashes can cause side effects.
- Your dentist can provide personalized advice on dental care.
Causes of Mouth Bleeding
Mouth bleeding often results from injuries such as falls or facial impacts. Mouth conditions like angular cheilitis and mouth ulcers can also cause bleeding.
Angular Cheilitis: This condition leads to cracked, split, and sore lips, along with pain when opening the mouth. Prevention tips include:
- Staying hydrated by drinking water
- Using lip balm and ointment
- Practicing good dental care
Consult your doctor or pharmacist for additional advice.
Mouth Ulcers: Typically, these heal without treatment. For pain relief, ask your doctor or pharmacist about appropriate ointments.
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- A sore or ulcer lasting more than two weeks
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking
- Repeated mouth bleeding
- Red or white patches in your mouth
- Swelling or numbness in the mouth
Bleeding After Dental Treatment or Injury
If you experience bleeding following dental treatment or an injury, consider these steps:
- Apply pressure over the area with gauze or a clean, rolled-up, dampened cotton handkerchief.
- Keep the pad in place for 30 minutes without removing it. If bleeding continues, repeat the process until you can see a dentist.
- Avoid rinsing your mouth or putting your fingers in your mouth.
- For pain, seek advice on suitable pain relief medications.
- Refrain from strenuous activities.
- Avoid hot drinks and hard foods. Cold foods like yogurt may be easier to eat and can provide pain relief.
- Smoking can irritate your mouth. Try to reduce or quit smoking.
- Follow any specific advice from your dentist regarding mouth rinsing and eating or drinking after dental procedures.
Summary
Good dental hygiene is crucial for preventing not only gum disease but also other oral health issues. Regular dental check-ups, a balanced diet, and avoiding excessive sugar can help maintain overall oral health. For those who have persistent issues despite good oral care, consulting a dental specialist may provide insights into underlying health issues that might need addressing.
Maintaining oral health is essential for overall well-being. Proper dental care practices, timely medical advice, and lifestyle adjustments can prevent and manage bleeding gums and other oral health problems effectively.












